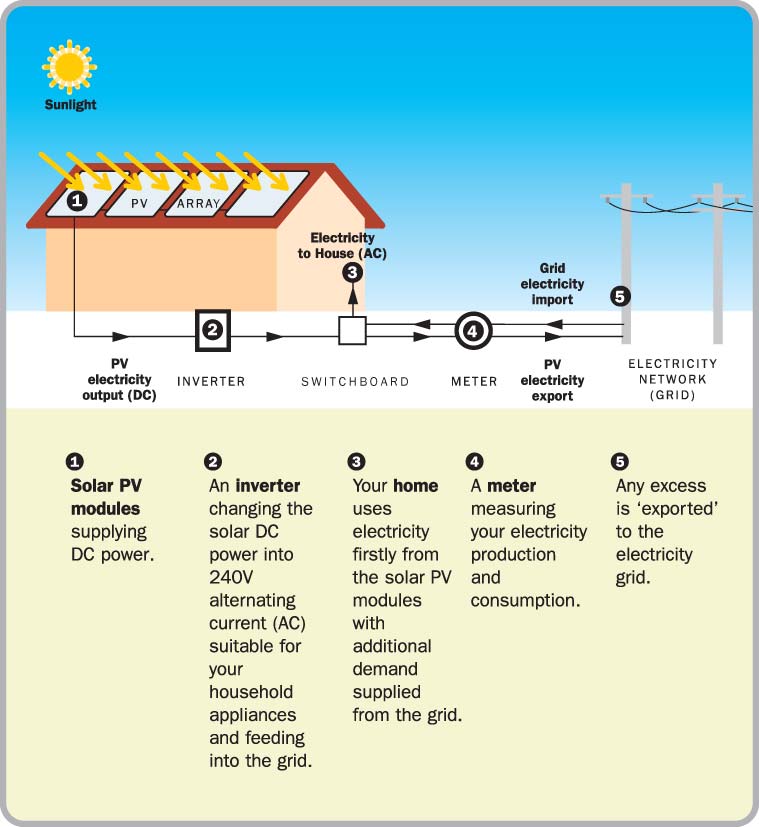
HOW SOLAR WORKS
Most solar power systems use PV modules (panels) installed on a rooftop to create and collect energy from sunlight.
Solar cells are produced from thin wafers of silicon. When light falls on the cells an electric current is produced. A collection of solar cells connected together forms a module.
An inverter converts the Direct Current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into Alternating Current (AC), the form of electricity conventionally used in homes.
You will need an inverter to convert the direct current (DC) power collected by the solar panels into power for your home, or power to send back to the electricity grid. It can be placed inside or outside your home and can give you information about the amount of electricity being produced by your system.
Meters and the grid

Solar PV modules supplying DC power.

An inverter changing the solar DC power into 240V alternating current (AC) suitable for your household appliances and feeding into the grid.

Your home uses electricity firstly from the solar PV modules with additional demand supplied from the grid.

A meter measuring your electricity production and consumption.

Any excess is 'exported' to the electricity grid.